Shard 的數量與 Rollover & Shrink API
前言
當我們將資料 Indexing 進入 Elasticsearch 後,隨著時光的飛逝,我們 Index 裡的資料通常也會愈來愈多,這時如何有效的管理資料就是一件很重要的事,這個主題的文章會來介紹 Index 管理的 Best Practices,這篇文章會著重在 Index 中 Shard 的數量配置方式及優化的方法。
進入此章節的先備知識
知道什麼是 Elasticsearch Index、Alias、Index Template。
初步了解 Lucene, Shard, Segment Files。
此章節的重點學習
Shard 的數量該怎麼設定。
隨著時間的變化,如何透過 Rollover API 及 Shrink API 來優化 Elasticsearch 中的 Indices。
Shard 的重要觀念
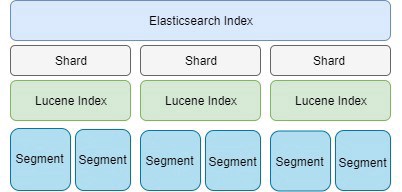
在一開始我們說明一下 Shard 的幾個重要的觀念:
Shard 是 ES Cluster 中切分資料來儲存的最小單位,裡面是透過 Lucene 管理的一群 Segment Files,也就是 Lucene Index。
Shard 的大小與數量:
最大多大?: 沒有一定的限制,主要是依照 Elasticsearch Cluster 硬體的性能來決定,早期官方文件是寫建議 10G,但忘了從哪個版本開始(應該有二、三年前),文件上已改成 20~40G,隨著硬體規格的成長、Elasticsearch 版本演進時效能不斷的優化,這個數字會需要實際測試才知道,以我實際的經驗,200G以上的 shard 也有遇到過。
最小多小?: 如果要設多個 shard 的話,
最好不要小於 1G,否則這時候切 shard 的好處太少,不如不要切 shard。數量多的好處?: 數量愈多的話,好處是資料量非常大時可以分散到多個 Node 去儲存、又或是有大量的 Indexing 的需求可以讓多個 Node 去分擔,若是單一 Shard 的儲存空間足夠,又沒有大量 Indexing 的需求時,應該讓 Shard 大一些,並且數量少一點會比較好。
數量少的好處?: 數量愈少其實處理搜尋的效能會較好,但取捨是當 Cluster 要 Rebalancing 時,一個巨大的 Shard 要搬移的成本很高。
Index 的管理方式
若你的資料量是固定的、或是成長非常緩慢的,請直接依照上述 shard 的觀念、硬體規格、成長規劃來設定 shard 的數量,以下著重在介紹隨著時間成長的資料的 Index 管理方式。
隨著時間增長的資料,資料要能分散存取的話,官方建議使用 time-based indices 來進行資料的管理,而不是在一開始設定大量的 shard 數量來期待之後資料的成長,因為 shard 的數量在建立 Index 時設定好之後,就不能再修改。
Elasticsearch 6.x 版之前,預設的 shard 數量是 5,但是從 7.x 版開始,預設的 shard 數量已改成 1,官方建議使用 time-based indices 來處理隨時間成長的資料。
Index 的數量太多的成本?
Index 的資訊是存在 Cluster stats 中,如果 Index 數量太多 (特別是 Mapping 欄位又很多時),會讓 Cluster stats 變很大,這會佔用 JVM heap size,也會造成 update 這種需透用到 cluster stats 資訊來確保處理一致性的請求效能變慢。
針對 time-based indices 的管理方式 - Rollover Pattern
一般這種資料我們的期待與使用情境如下:
在 indexing 大量資料時,為了有較好的效能,我們一開始會將 shard 數量提高。
當資料趨近穩定、不太會變動時,我們為了要有更好的查詢效能,我們會希望 shard 的數量愈少愈好,但也不要到太肥大的狀態。
有時可能覺得一天一個 Index 會比較好照時間來管理過期的資料,但每天的資料量可能不一定,Shard 的數量又不見得都適合套用同一套規則。
因此這時官方的 Rollover & Shrink 會是很好的解決方案,這個 Rollover Pattern 的基本運作如下:
定一個 indexing 新文件專用的 Alias ,並將他指到目前 active index。
定另一個 searching 用的 Alias,指定所有不論新、舊的 indices。
active index 可以指定有很多個 shard,讓寫入的效能能最佳。
當 active index 資料量達到一個條件、或是時間過太久了,會進行 Rollover,產生一個新的 index 成為 active index,並把 indexing 用的 alias 指向他。
舊的 index 被搬到 code node,並觸發 Shrink 的動作,將他轉成單一 shard 的 index,並且觸發 forced-marged 和 compression ,以進行資源的優化。
以下分別針對 Rollover API 及 Shrink API 來示範 Rollover Pattern 的實作:
Rollover
建立一個 index - logs-000001 與指向他的 alias - logs_write:
使用 Rollover API 建立 超過7天 或 滿1000筆文件 要觸發自動 rollover:
Rollover 的規則,會依照 index 名字後有
-而且接著數字,就會接受這是要 Rollover 的 index,但長出來新的 index 會依照這邊的定義,會是六位數並且會補 0 的格式。例如當筆數滿 1000 後,會產生新的 index
logs-000002。
若新的 index 不是這個名命的規則,可以明確的指定名字。
Shrink
Shrink 的 API 主要的目的就是把 index 的 shard 數量變少,而變少的規則,必需是原來數值的因數,例如原本是 8 ,那只能 shrink 成 4 或 2 或 1、原本是 15 的話,只能 shrink 成 5 或 3 或 1。
運作機制如下:
建立一個新的 index,其設定會完全照之前的 index,只有 shard 數量是變少的,此時 index 的狀態會先保持
_close。透過 OS 的 hard-links 來合併 shards ,如果 OS file system 不支援,會直接用複製的方式將 shard 複製到新的 index 裡。
最後再將新的 index 重新 open。
Shrink API 如下:
另外也可以宣告一些類似 create index API 能指定的參數:
透過這些設定,就能指定 shrink 成特定數量的 shards 了。 (不過要記得必須是原來 shard 數量的因數才行。)
參考資料
Last updated